News Center
Key points for Selecting Power supply and Distribution Materials in Clean workshops
2025/11/6
1 conductor matching
Youdaoplaceholder0 Copper conductors are preferred for critical circuits (with excellent electrical conductivity and strong mechanical properties), and aluminum conductors can be selected for long-distance power transmission to reduce costs; The cross-sectional area of the conductor needs to be determined by calculating the load current (three-phase current formula: I = P/(√3 × U × cosφ)), and the current-carrying capacity should be corrected in combination with the laying method and the ambient temperature.
Youdaoplaceholder0 2. Insulation and sheath
Conventional scenarios : Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) insulation is superior to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), with high temperature resistance and stable electrical performance;
High-temperature/fireproof zone : Select A-class flame-retardant cables (self-extinguishing time after removal from the fire source ≤5 seconds), and fire protection lines must use low smoke zero halogen type (low toxicity of combustion smoke).
Damp/corrosive environment : The sheath should be resistant to acid and alkali (such as PTFE material). For direct burial, an armor layer should be added to resist mechanical damage.
3. Voltage level
The rated voltage of the cable (such as 0.6/1kV, 8.7/15kV) must be higher than the maximum working voltage of the system. The thickness of the insulation layer in high-voltage scenarios (> 110kV) should be specially designed according to the electrical strength (≥20kV/mm).
02 scenario-based adaptation
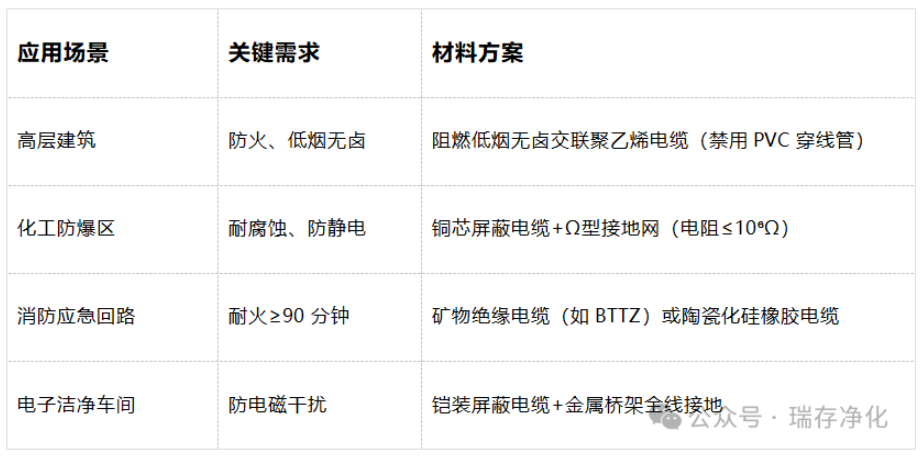
03 Installation and Economy
1. Laying protection
The cable filling rate inside the cable tray should be no more than 40% (to ensure heat dissipation), and the bending radius of the conduit should be greater than 6 times the diameter of the cable. For directly buried cables, sand covers should be laid (to prevent mechanical damage), and IP68-level waterproof sleeves should be used in damp tunnels.
2, cost optimization
Aluminum core cables can be used for low-voltage non-critical circuits to reduce costs (30%-40% lower than copper). Cable trays are selected from galvanized steel plates (thickness ≥1.2mm) or fiberglass reinforced plastic (for anti-corrosion scenarios) based on their load-bearing capacity.
04 Mandatory safety clause
Medical/data center power distribution cabinets must be equipped with IT isolation power supply systems (to prevent electric leakage injuries). Anti-static areas (such as laboratories) should use anti-static flooring (with a surface resistance of 10⁶-10⁹Ω) and grounding electrodes (depth ≥2.5m). All grounding main lines have a cross-sectional area of no less than 95mm² (made of copper), and the connection spots should be welded to prevent loosening. 05 summary Selection should be based on voltage level, current carrying capacity, and environmental corrosiveness as prerequisites. In high-risk scenarios, additional fire prevention/explosion-proof requirements should be imposed (mineral cables for fire protection and shielded cables for workshops), taking into account both laying costs and grounding reliability.






