News Center
Summary of Knowledge on Pressure Pipeline layout design
2025/9/2
Pressure pipelines are classified as special equipment. According to the definition in the "Regulations on Safety Supervision of Special Equipment", they refer to tubular equipment that uses a certain pressure to convey gases or liquids. The scope is defined as pipelines carrying gas, liquefied gas, steam media or flammable, explosive, toxic, corrosive liquid media with a maximum working pressure greater than or equal to 0.1MPa(gauge pressure) and a maximum working temperature higher than or equal to the standard boiling point, with a nominal diameter greater than 25mm.
For a single pressure pipeline, the working principle is to rely on external power or the driving force of the medium itself to transport the medium at the source of the pressure pipeline to its end.
Characteristics of Pressure pipelines
1. Pressure pipelines form a system that is interrelated and mutually influential, with any slight change affecting the entire situation.
2. Pressure pipelines have a large length-to-diameter ratio and are highly prone to instability, with more complex force conditions than pressure vessels.
The fluid flow state inside pressure pipelines is complex, with a small buffer margin. The frequency of working condition changes is higher than that of pressure vessels (such as high temperature, high pressure, low temperature, low pressure, displacement and deformation, wind, snow, earthquakes, etc., all of which may affect the force conditions of pressure pipelines).
3. There are numerous types of pipe components and pipe supports, and each material has its own characteristics and specific technical requirements, making the selection of materials complex.
4. There are more possible leakage points on pipelines than on pressure vessels. Usually, there are five for a single valve.
5. Pressure pipelines come in a wide variety and large quantity, with numerous design, manufacturing, installation, inspection, and application management processes, which are quite different from pressure vessels.
The uses of pressure pipelines
Conveyed medium (Main uses)
Storage function (for long-distance pipelines)
Heat exchange (for industrial pipelines)
Design steps for pressure pipelines
1. Select the pipe material based on the type of medium, pressure and temperature.
2. Calculate the pipe diameter and wall thickness, and compile or determine the pipe grade table.
3. Develop pipeline layout plans, determine pipeline directions and laying methods.
4. Draw the pipeline layout diagram and axial side diagram.
5. Prepare the pipeline characteristic table.
6. Conduct stress, thermal compensation and support thrust calculations.
7. Provide civil engineering data to relevant specialties.
8. Complete the design drawings and conduct the drawing co-signature.
Layout of pressure pipelines
How to determine design pressure in design problems?
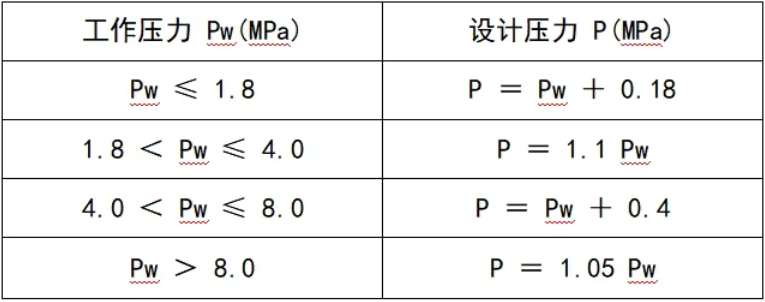
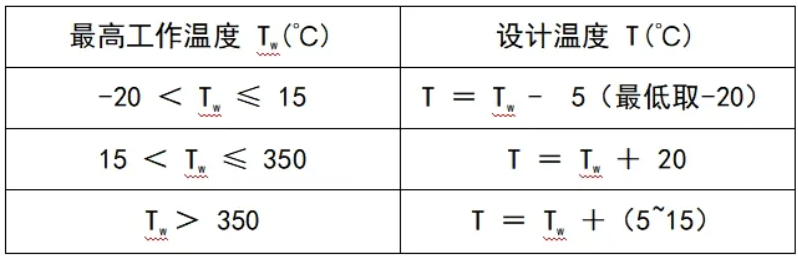
How to determine the design temperature?
1. Pipelines should be laid overhead as much as possible. If necessary, they can also be buried underground or laid in trenches. (Easy to install, produce and maintain
2. Try to use the hanger design as much as possible to bring the pipeline as close as possible to the existing buildings and structures, but avoid having components with high flexibility bear large loads.
3. Pipelines should not be laid within the range of hoisting holes in buildings, the areas where internal components of equipment are withdrawn, and the areas where flanges are removed.
4. Pipeline layout should be carried out in parallel rows, with straight lines as much as possible and fewer turns and intersections. This can reduce the number of pipe racks, save materials, and be aesthetically pleasing and easy to install.
5. Pipes should be arranged in concentrated rows as much as possible. The bottom of bare pipes should be aligned with the ground of pipe supports to facilitate the design of supports.
6. When the elevation or direction of the pipeline changes, it is necessary to avoid the formation of "bags" of accumulated gas or liquid in the pipeline. If this cannot be avoided, exhaust valves should be installed at high points and liquid discharge valves at low points.
7. When pipelines are laid in a plane, they should have a slope. The direction of the slope is generally the same as the flow direction of the material, but there are exceptions, which are determined according to the specific process.
8. No components that may leak, such as flanges, threaded joints, and compensators with packing, should be installed on the pipelines above roads and railways.
9. When pipes pass through roofs, floors, platforms and walls, they generally need to be protected by sleeves.
10. Buried pipelines should take into account the influence of vehicle loads. When crossing roads, sleeves should be added, and the distance between the pipe top and the road surface should be no less than 0.6 meters, and it should be below the depth of frozen soil.
When connecting a branch pipe from a horizontal gas main pipe, it should be led out from the top of the main pipe.
12. For the layout of multi-layer co-laid pipelines, gas pipelines, heat pipelines, public utility pipelines and electrical instrument troughs should be placed on the upper layer, while corrosive medium pipelines and low-temperature pipelines should be placed on the lower layer.
Pipelines carrying flammable, explosive, toxic and corrosive materials should not be laid in living quarters, staircases, corridors and other places. The vent pipe should be led to the designated outdoor location or 2 meters above the roof.
14. Pipes without insulation layers do not require pipe supports or brackets. Large-diameter thin-walled bare pipes and pipes with insulation layers should be supported by pipe supports or brackets.
15. The conditions for the direct burial of pipelines are:
① Pipelines that convey non-toxic, non-corrosive and non-explosive media and for which they cannot be laid on the ground for some reason.
② Process medium pipelines related to underground storage tanks or underground pump rooms.
③ Cooling water and fire-fighting water or foam fire-fighting pipes.
④ Thermal pipelines with operating temperatures below 150℃.
Principles for selecting common materials for pressure pipelines
The use of common pipe materials for pressure pipelines is determined by the operating conditions of the conveyed medium (such as pressure and temperature) and the characteristics of the medium under those conditions.
Consider the following factors:
Preferred pipe materials:
When choosing pipe materials, metal materials are generally considered first. If metal materials are not suitable, non-metal materials are then taken into account. Steel pipes should be given priority for metal materials, and non-ferrous metal materials should be considered later. Among steel pipes, carbon steel should be considered first. When not applicable, stainless steel can be selected. When considering carbon steel materials, welded steel pipes should be given priority. If not, seamless steel pipes should be selected.
The influence of medium pressure
The higher the pressure of the conveyed medium is, the thicker the wall thickness of the pipe will be, and the requirements for the pipe material are generally also higher.
When the medium pressure is above 1.6MPa, seamless steel pipes or non-ferrous metal pipes can be selected.
2. When the pressure is very high, such as in the production of ammonia synthesis, urea and methanol, the medium pressure of some pipes can reach up to 32MPa. Generally, high-pressure seamless steel pipes made of 20 steel or 15MnV are selected.
3. Tubes on vacuum equipment and oxygen tubes with a pressure greater than 10MPa are generally made of copper and brass tubes.
When the medium pressure is below 1.6MPa, welded steel pipes, cast iron pipes or non-metallic pipes can be considered. However, the pressure of the medium that cast iron pipes can withstand must not exceed 1.0MPa. The medium pressure that non-metallic pipes can withstand is related to the type of non-metallic material. For example, the operating pressure of rigid polyvinyl chloride pipes is less than or equal to 1.6MPa. Reinforced polypropylene pipes, with a usage pressure of less than or equal to 1.0MPa; ABS pipes, with a usage pressure of less than or equal to 0.6MPa.
5. For water pipes, when the water pressure is below 1.0MPa, welded steel pipes made of Q235A material are usually adopted. When the water pressure is greater than 2.5MPa, seamless steel pipes made of 20 steel are generally used.
The influence of the chemical properties of the medium
The influence of the chemical properties of the medium is mainly reflected in corrosion and should be given high attention.
1. The medium is neutral and generally has low requirements for materials. Ordinary carbon steel pipes can be selected.
2. If the medium is acidic or alkaline, acid or alkali resistant pipes should be selected.
3. For the transportation of water and water vapor, carbon steel pipes are used.
The influence of the pipe's own function:
Some pipes, in addition to having the function of transporting media, also need to have the functions of shock absorption, absorbing thermal expansion and contraction, and being able to move frequently under working conditions.
The influence of pressure drop
After the material of the pipe is initially selected, the pressure drop of the pipeline needs to be calculated to determine the inner diameter of the pipe. By calculating the pressure drop, check whether the selected material meets the requirements. Especially when initially selecting plastic pipes, it is even more important to pay attention to the recheck of pressure drop.






